Athlete’s foot is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet, particularly between the toes. It develops in warm, moist environments and is commonly caused by walking barefoot in public showers, locker rooms, or around pools. Risk factors include wearing tight or non-breathable shoes, excessive sweating, and compromised immune function. Symptoms often include itching, redness, peeling, burning, and cracking of the skin. Preventive measures include keeping feet clean and dry, changing socks regularly, wearing breathable shoes, and avoiding walking barefoot in shared spaces. A podiatrist can diagnose athlete’s foot, provide effective antifungal treatment, and recommend strategies to prevent recurrence. If you notice persistent itching or skin changes on your feet, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist who can treat this condition, which may include prescribed medication.
Athlete’s foot is an inconvenient condition that can be easily reduced with the proper treatment. If you have any concerns about your feet and ankles, contact one of our podiatrists from Columbus Podiatry & Surgery. Our podiatrists will treat your foot and ankle needs.
Athlete’s Foot: The Sole Story
Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, can be an extremely contagious foot infection. It is commonly contracted in public changing areas and bathrooms, dormitory style living quarters, around locker rooms and public swimming pools, or anywhere your feet often come into contact with other people.
Solutions to Combat Athlete’s Foot
- Hydrate your feet by using lotion
- Exfoliate
- Buff off nails
- Use of anti-fungal products
- Examine your feet and visit your doctor if any suspicious blisters or cuts develop
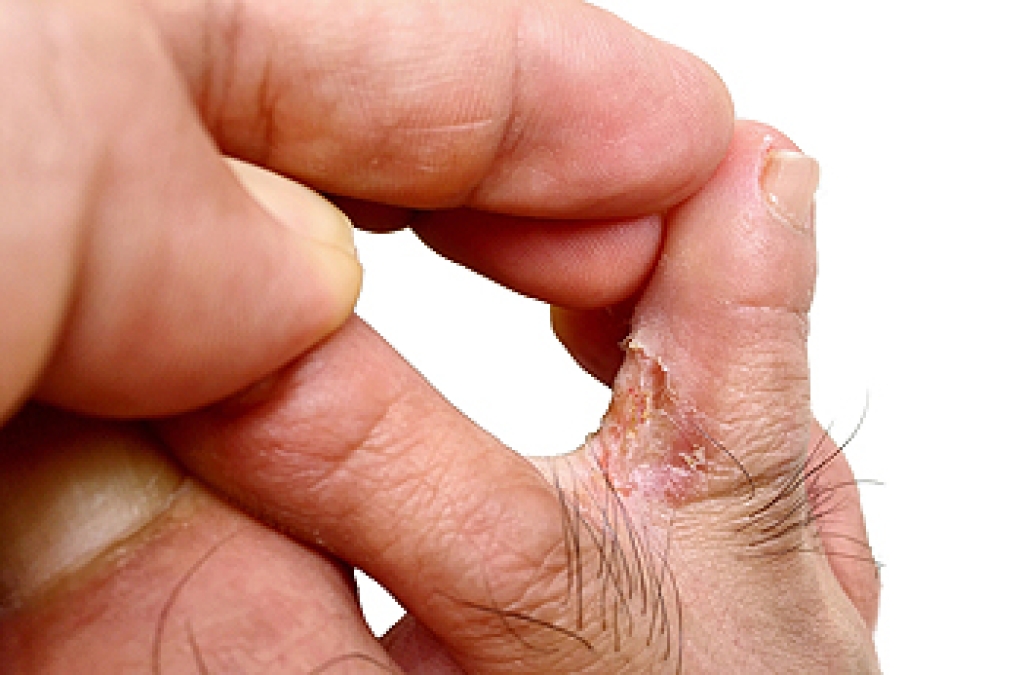
Athlete’s foot can cause many irritating symptoms such as dry and flaking skin, itching, and redness. Some more severe symptoms can include bleeding and cracked skin, intense itching and burning, and even pain when walking. In the worst cases, Athlete’s foot can cause blistering as well. Speak to your podiatrist for a better understanding of the different causes of Athlete’s foot, as well as help in determining which treatment options are best for you.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our office located in Columbus, OH . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.